Tweepository
The Tweepository plugin enables the repository to harvest a stream of tweets from a twitter search. This document applies to Tweepository 0.3.1.
Contents
Installation Prerequisites
The following perl libraries must be installed on the server before the Bazaar package will function.
Data::Dumper Date::Calc Date::Parse Encode HTML::Entities JSON LWP::UserAgent Number::Bytes::Human Storable URI URI::Find
Installation
Install through the EPrints Bazaar
Setting Up Cron Jobs
There are two processes that need to be regularly run. Due to the heavyweight nature of these tasks, they should be put into the crontab rather than being handled by the EPrints Indexer. However, they have been created as event plugins for future inclusion in the indexer. Two wrapper scripts have been created in the plugin directory. You may need to modify the top line of each script to the install location of EPrints:
#!/usr/bin/perl -I/opt/eprints3/perl_lib
use strict;
use warnings;
use EPrints;
my ($repoid) = @ARGV;
die "update_tweetstreams.pl *repositoryid*\n" unless $repoid;
chomp $repoid;
my $ep = EPrints->new;
my $repo = $ep->repository($repoid);
die "couldn't create repository for '$repoid'\n" unless $repo;
my $plugin = $repo->plugin('Event::UpdateTweetStreams');
$plugin->action_update_tweetstreams;
add the following to your eprints crontab (assuming EPrints is installed in '/opt/eprints3'):
*/20 * * * * /opt/eprints3/lib/plugins/EPrints/Plugin/Event/update_tweetstreams.pl REPOSITORYID 50 0 * * * /opt/eprints3/lib/plugins/EPrints/Plugin/Event/update_tweetstream_abstracts.pl REPOSITORYID
Using
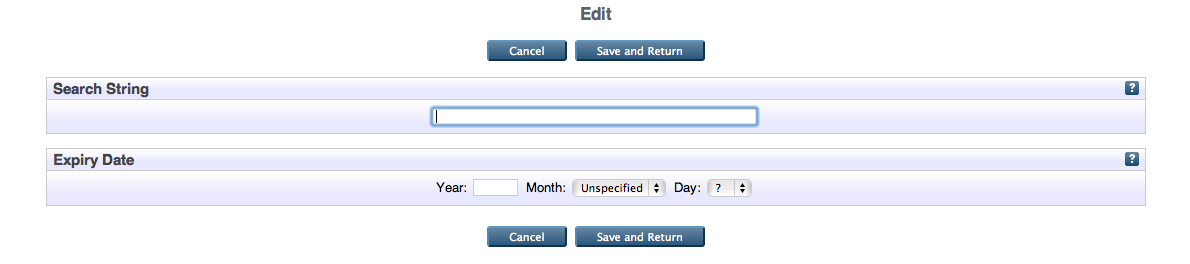
To create a new tweetstream, click on 'Manage Records', then on 'Twitter Feed', and then on the 'Create new Item' button. A new tweetstream object will be created, and you will need to enter two parameters:
- Search String: Passed directly to Twitter as the search parameter.
- Expiry Date: The date on which to stop harvesting this stream.
Once these fields have been completed, click 'Save and Return'.
Harvesting
Every 20 minutes, the tweepository package will harvest each stream. No harvesting is done on creation, to the tweetstream will initially be empty. Tweets will be processed to:
- extract hashtags
- extract mentioned users
These data will be summarised in the tweetstream objects.
URLs
Note that URLs are no longer followed to expand shortened links. This is a target for future development.
Viewing a Tweetstream
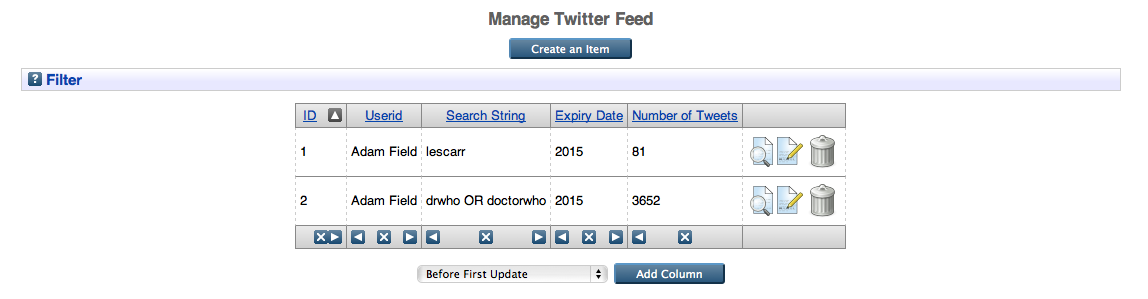
To view a tweetstream, click on 'Manage Records', then 'Twitter Feed':
The above screen shows a list of all twitter streams that the logged in user has access to. Clicking on the view icon (the magnifying glass) will bring up the view screen, which shows all metadata set on this twitter feed. At the top of the page will be a link to the tweetstream's page. It will be of the form:
http://repository.foo.com/id/tweetstream/5
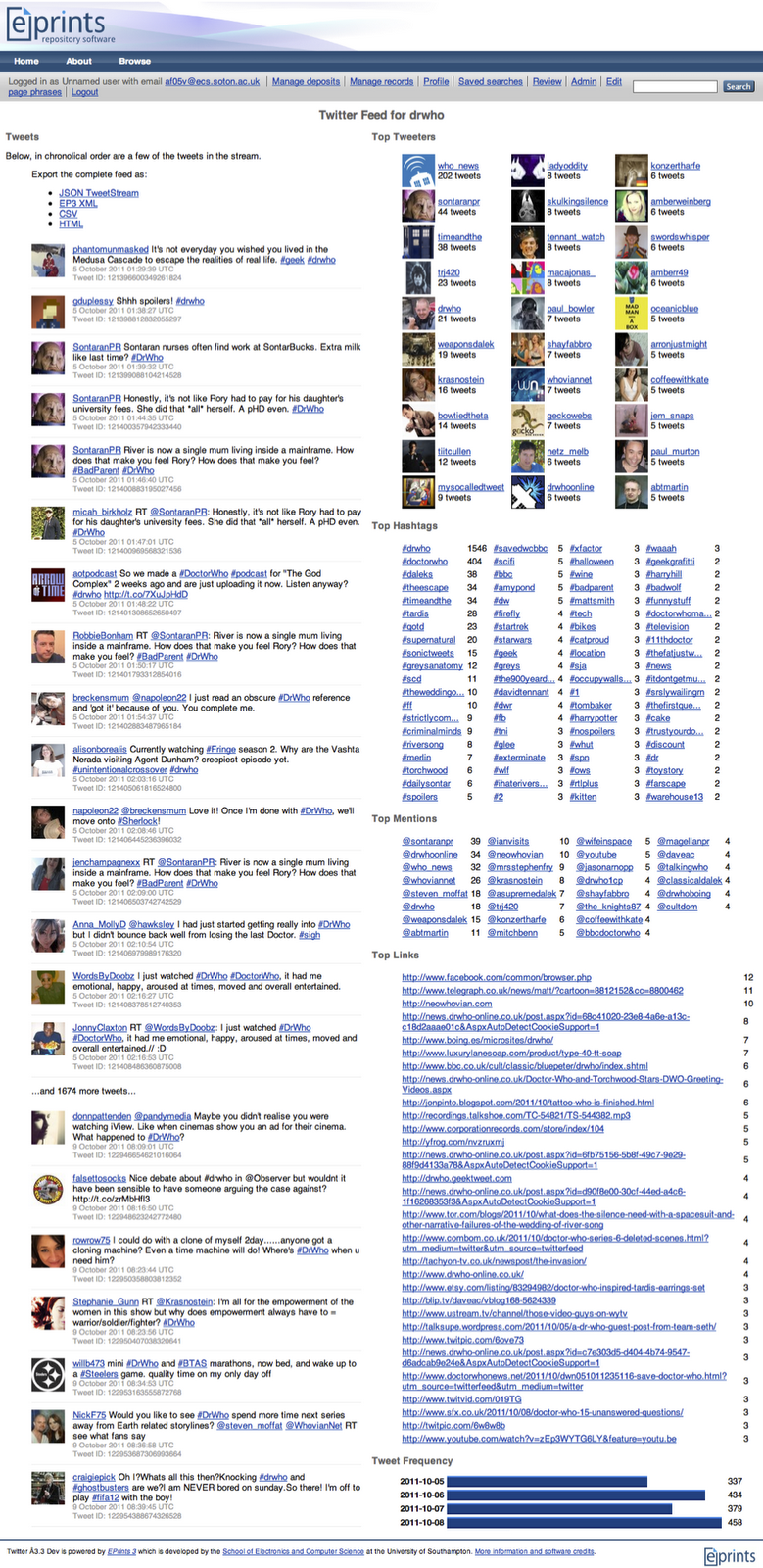
Below is an example of a tweetstream page:
Exporting
Due to the architecture of the twitter feeds (see below), exporting using the standard eprints exporters (e.g. XML) will only work if both the tweet dataset and the tweetstream dataset are both exported. For this reason, export plugins have been provided for tweetstreams. Currently, a tweetstream can be exported as:
- CSV
- HTML
- JSON
Note that EPrints may struggle to export very large tweetstreams through the web interface. If there are more than several hundred thousand tweets, it may be advisable to export from the command line.
Architecture
Both tweetstreams and tweets are EPrints Data Objects. Each tweet object stores the ID of all tweetstreams to which it belongs. This allows tweets to appear in more than one stream, but only be stored once in the database.
Permissions
The z_tweepository_cfg.pl file contains the following:
$c->{roles}->{"tweetstream-admin"} = [
"datasets",
"tweetstream/view",
"tweetstream/details",
"tweetstream/edit",
"tweetstream/create",
"tweetstream/destroy",
"tweetstream/export",
];
$c->{roles}->{"tweetstream-editor"} = [
"datasets",
"tweetstream/view",
"tweetstream/details:owner",
"tweetstream/edit:owner",
"tweetstream/create",
"tweetstream/destroy:owner",
"tweetstream/export",
];
$c->{roles}->{"tweetstream-viewer"} = [
"tweetstream/view",
"tweetstream/export",
];
push @{$c->{user_roles}->{admin}}, 'tweetstream-admin';
push @{$c->{user_roles}->{editor}}, 'tweetstream-editor';
push @{$c->{user_roles}->{user}}, 'tweetstream-viewer';
This defines three roles. The admin role:
- Can create tweetstreams
- Can destroy tweetstreams
- Can see tweetstream details
- Can see the list of tweetstreams in 'Manage Records'
- Can view tweetstream abstract pages
- Can export tweetstreams
The editor role:
- Can create tweetstreams
- Can destroy tweetstreams that they created
- Can see details of tweetstreams that they created
- Can see the list of tweetstreams in 'Manage Records'
- Can view tweetstream abstract pages
- Can export tweetstreams
The viewer role:
- Can view tweetstream abstract pages (but need to know the URL)
- Can export tweetstreams
These three roles have been assigned to repository administrators, editors and users respectively. This can be changed by modifying this part of the config.